
|
Valentin Nigolian, Ph.D. Room 102 Email: valentin.nigolian@unibe.ch |

We present a novel algorithm to map ball-topology tetrahedral meshes onto star-shaped domains with guarantees regarding bijectivity. Our algorithm is based on the recently introduced idea of Shrink-and-Expand, where images of interior vertices are initially clustered at one point (Shrink-), before being sequentially moved to non-degenerate positions yielding a bijective map (-and-Expand). In this context, we introduce the concept of the cluster mesh, i.e. the unexpanded interior mesh consisting of geometrically degenerate simplices. Using local, per-vertex connectivity information solely from the cluster mesh, we show that a viable expansion sequence guaranteed to produce a bijective map can always be found as long as the mesh is shellable. In addition to robustness guarantees for this ubiquitous class of inputs, other practically relevant benefits include improved parsimony and reduced algorithmic complexity. While inheriting some of the worst-case high run time requirements of the state of the art, significant acceleration for the average case is experimentally demonstrated.
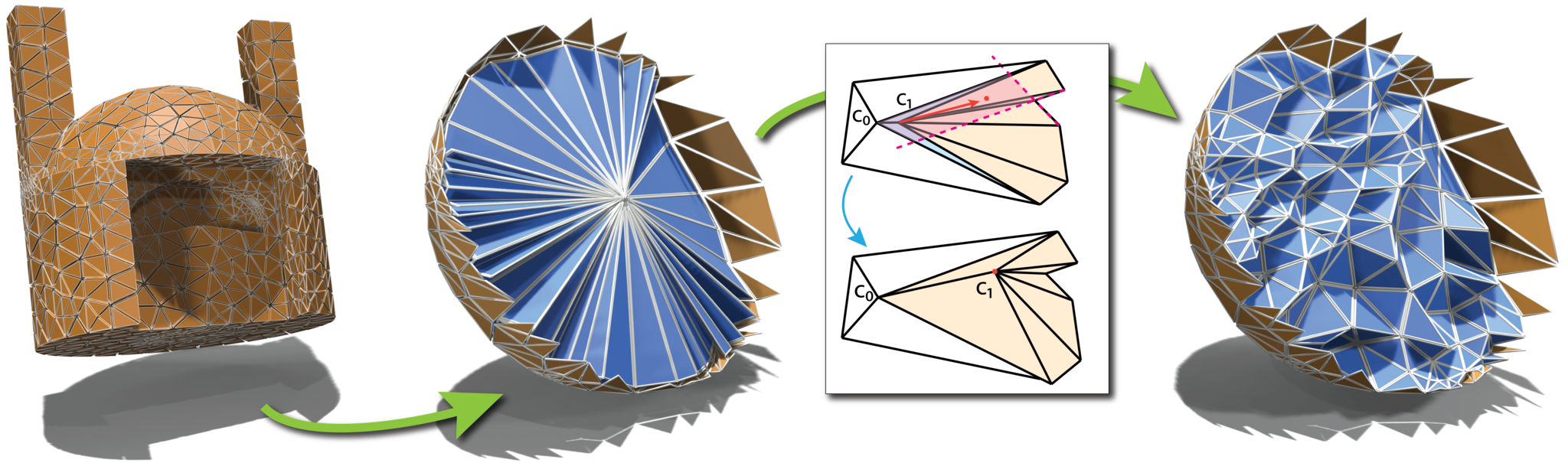
Volumetric mapping is a ubiquitous and difficult problem in Geometry Processing and has been the subject of research in numerous and various directions. While several methods show encouraging results, the field still lacks a general approach with guarantees regarding map bijectivity. Through this work, we aim at opening the door to a new family of methods by providing a novel framework based on the concept of progressive expansion. Starting from an initial map of a tetrahedral mesh whose image may contain degeneracies but no inversions, we incrementally adjust vertex images to expand degenerate elements. By restricting movement to so-called expansion cones, it is done in such a way that the number of degenerate elements decreases in a strictly monotonic manner, without ever introducing any inversion. Adaptive local refinement of the mesh is performed to facilitate this process. We describe a prototype algorithm in the realm of this framework for the computation of maps from ball-topology tetrahedral meshes to convex or star-shaped domains. This algorithm is evaluated and compared to state-of-the-art methods, demonstrating its benefits in terms of bijectivity. We also discuss the associated cost in terms of sometimes significant mesh refinement to obtain the necessary degrees of freedom required for establishing a valid mapping. Our conclusions include that while this algorithm is only of limited immediate practical utility due to efficiency concerns, the general framework has the potential to inspire a range of novel methods improving on the efficiency aspect.
